Distinguishing Between Fleas and Bed Bugs: Identifying Your Pest Predicament
Don’t let fleas and bed bugs take over your home. Our experienced insured and bonded trained exterminators at Maximum Pest Control Services will get rid of them for good, so you can enjoy a clean pest-free living space. Contact Us Today (905) 582-5502.
Discovering tiny biting insects in your home is alarming. But before you freak out, inspect closely and identify the pest. Telling the difference between fleas and bed bugs provides clues to address the proper infestation. Eliminating these blood-sucking freeloaders requires an accurate diagnosis.
Though they overlap in some behaviors, fleas and bed bugs have distinct characteristics. Learn to distinguish these pests through appearances, habits, bites, and other evidence. Accurate identification is the critical first step to ridding your home of unwelcome biting bugs.
Appearance and Size
Fleas and bed bugs are both tiny, wingless insects equipped for jumping and sucking blood. But they have notable physical differences:
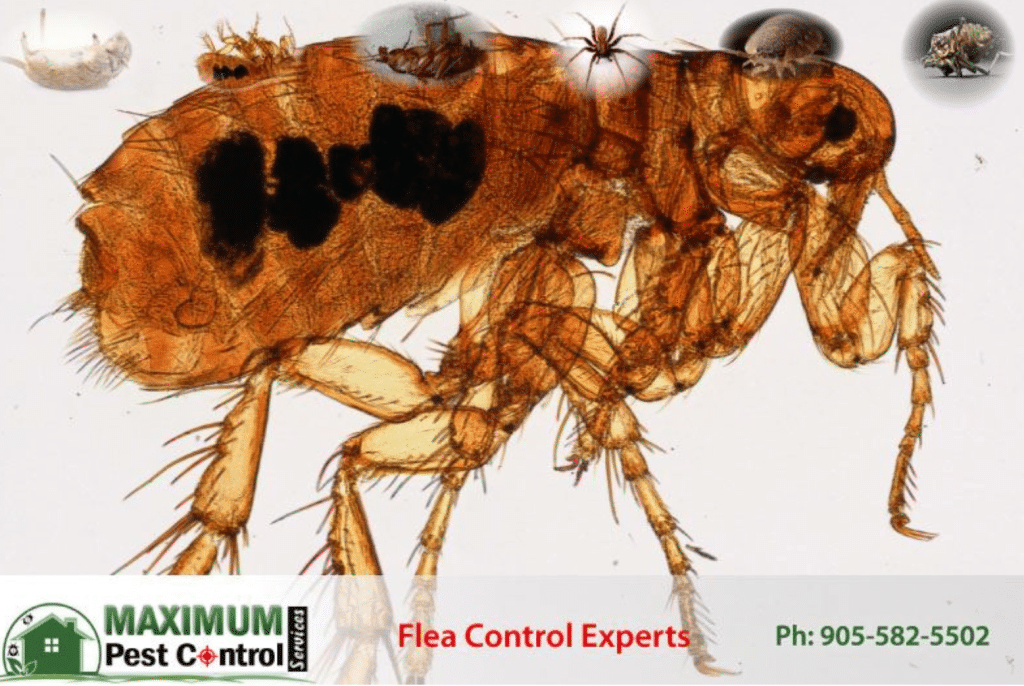
What Do Fleas look Like?
- Tiny oval-shaped bodies, 1/16 to 1/8 inches’ long
- Narrow heads with mouthparts adapted for piercing skin.
- Powerful rear legs for jumping long distances.
- Dark brown to blackish in color; may appear reddish after a blood meal.
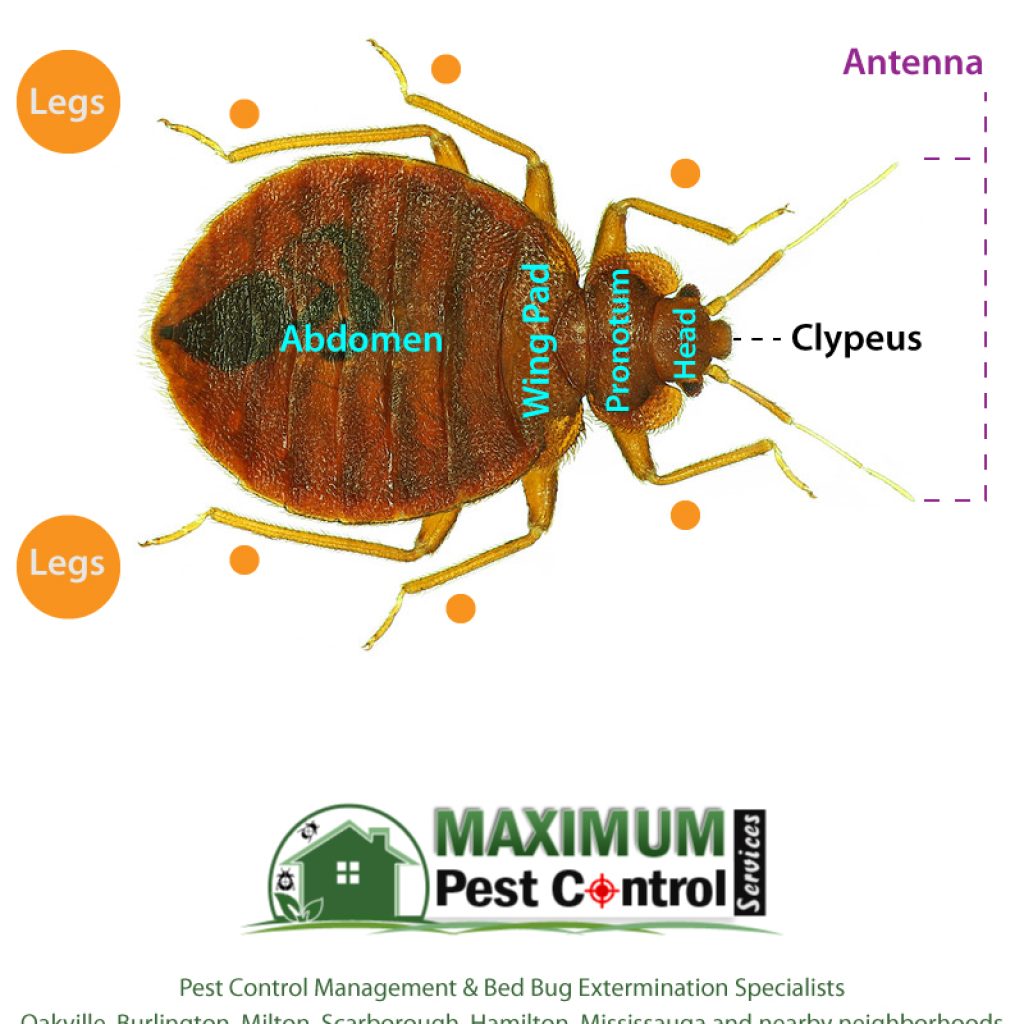
Bed Bugs
- Broad, flat bodies, 1/4 to 5/8 inches’ long
- Short, wide heads with mouths for sucking blood
- Vestigial wing pads but cannot fly.
- Short, stubby legs lacking jump power.
- Reddish-brown to brown; swollen and darker red after feeding.
Behavior and Habits
These bloodsuckers also differ in their behaviors:
Fleas
- Jump rapidly making them hard to catch.
- Bite hosts briefly and quickly flee.
- Prefer furry animal hosts like cats, dogs, rodents, birds.
- Feed repeatedly each day to survive.
- Live in animal bedding, carpets, upholstery
- Travel quickly between animal nests and humans.
Bed Bugs – Where Bedbugs Hide?
- Crawl slowly and hide effectively.
- Bite painfully and feed for 5-10 minutes.
- Feed chiefly on humans, occasionally bats and birds.
- 5-10 days feeding requirement only.
- Hide in bedroom furniture, floors, walls, textiles.
- Travel slowly between human sleeping areas.
Bites and Health Risks
These pests leave different bite marks and pose unique health threats:
Flea Bites
- Small, red, raised itchy spots often in clusters.
- Flea dirt (excrement) may appear as black specks.
- Can transmit typhus, plague, tapeworms, and other diseases.
- Large, swollen, red welts in zig-zag lines or clusters.
- Extremely itchy; may not appear for days after bite.
- No disease transmission but can cause infection from scratching.
Fleas leave tiny clustered red bumps while bed bugs make larger, inflamed raised welts. Fleas also come with more disease risks.
Evidence for Identification
Carefully examining your home can provide these clues to positively identify the pest:
Signs of Fleas
- Tiny black flea dirt (feces) peppering bedding and floors
- Small bloodstains from crushed fleas
- Flea eggs and larvae in animal bedding and carpets
- Quickly jumping bugs visible on floors and furniture
- Bites concentrated around ankles and legs.
- Dark or reddish fecal stains in harborage areas
- Shed white skins and eggshells in crevices.
- A musty odor in heavily infested rooms
- Visible bugs emerging at night to feed.
- Bites often concentrated on arms, neck, face.
- Blood stains, and quick jumps signal fleas. Bed bug skins, eggs, odor, and patterned bites point to bed bugs.
Effective Treatment Methods
Once identified, use these targeted strategies to eliminate infestations:
Treating Fleas (How to Get Rid of Fleas)
- Treat infested pets with flea meds and restrict contact.
- Vacuum extensively then dispose of bags immediately.
- Use pet-safe sprays and insect growth regulator (IGR) treatments.
- Treat carpets, floors, furniture, pet beds, and kennels
- Clean, treat, and seal outdoor areas pets frequent.
- Treat yard and kennel areas with sprays and beneficial nematodes
Treating Bed Bugs
- Inspect and meticulously seal crevices where they hide.
- Apply insecticides directly into harborage cracks and gaps.
- Treat mattresses thoroughly, encase them afterward.
- Use contact sprays, dusts, and steam on furniture and floors.
- Wash and heat treat infested clothing and bedding.
- Remove heavily infested furniture and mattresses.
Note: Fleas call for aggressive treatment of pets, bedding, carpets, yards. Bed bugs require targeting cracks and voids, mattresses, furniture, and clutter they hide in.
Preventing Re-infestations
After treatment, take precautions to avoid new infestations:
Flea Prevention Tips
- Keep pets on monthly flea prevention medications.
- Restrict pets from roaming yards and neighbor areas.
- Install flea traps around doors and potential entry points.
- Caulk cracks and install door sweeps to block access.
- Treat outdoor areas with sprays and beneficial nematodes
- Ask pet owners and visitors about flea issues before visits.
Bed Bug Prevention Tips
- When buying used furniture, should be examined before bringing it home.
- Seal crevices around bed frames, baseboards, and window frames.
- Ensure box springs and mattresses covered with bedbugs’ encasements.
- Install climb-up bed bug interceptors under furniture legs.
- Arrange beds away from walls and avoid bed skirts.
- Limit travel baggage in bedrooms and inspect after trips.
- Diligence in monitoring and exclusion will help keep these pests from re-establishing themselves.
Misidentifying Bites
Itchy welts and bites are often the first clue of an infestation. However, reactions can vary, and other insects or conditions may be mistaken for fleas or bed bugs. Some possible misdiagnoses:
- Mosquito bites – Appear as small, red, swollen marks that flare up shortly after bites. Very itchy.
- Spider bites – Painful red bumps with a blistered center. May take many days to develop.
- Scabies – Tiny burrows in the skin made by human itch mites. Intense itching and rash between fingers, wrists, elbows.
- Allergies – Small, round hives or itchy bumps resulting from allergic reactions. Typically appear suddenly within hours.
- Eczema – Patches of irritated, inflamed skin with severe itching. Often occurs on hands, feet, insides of elbows or backs of knees.
Don’t assume bites equal fleas or bed bugs. Properly identifying the pest is key to addressing the infestation correctly and avoiding pricey, ineffective treatments. When in doubt, consult pest experts.
Final Thoughts
Fleas and bed bugs both feast on blood and leave irritating bites. Learning their distinguishing traits is essential to managing infestations properly. Fleas are tiny jumping insects that briefly bite animal hosts then flee. Bed bugs are larger crawling bugs that gradually bite and remain on human hosts. Evidence like fecal spots, eggs, and bite patterns can further pinpoint the pest.
Accurate identification guides effective treatments like thorough vacuuming, proven insecticides, isolation, steaming, fumigation, and diligent exclusion techniques that will eliminate these blood-sucking freeloaders. Don’t live with biting mystery bugs. Contact Maximum Pest Control Services for complete bed bug or flea elimination from homes or businesses calling (905) 582-5502.